INTRODUCTION
Telehealth proved to be a boon during the pandemic
Telehealth is among the latest medical wonders, bringing seamless access to quality care over long distances at a patient’s convenience—transforming the healthcare sector by leaps and bounds.
While telehealth isn’t precisely a recent novelty— with its use in outpatient care already spanning decades—the ubiquity of portable computers and intelligent devices alongside the onset of broadband connections has pushed its adoption to even greater heights. Rapid digital infrastructure expansion isn’t the only catalyst for telehealth’s explosive popularity.
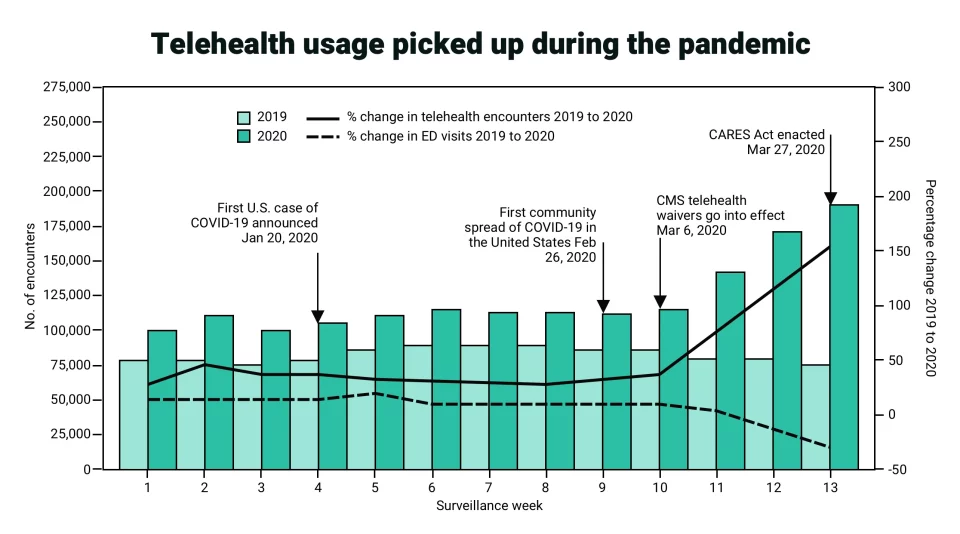
Number of telehealth patient encounters reported by four telehealth providers that offer services in all states and percentage change in telehealth encounters and emergency department visits — United States, January 1–March 30, 2019 (comparison period) and January 1–March 28, 2020 (early pandemic period)
The ongoing global health crisis due to the Coronavirus (COVID-19) has also opened up new possibilities for its uptake in various areas of medical care. Indeed, as efforts to curb viral transmission through social distancing and lockdown take greater precedence, there has been a shift in outlook on how routine check-ups and doctor visits are typically performed. In times when physical contact and public gatherings are greatly discouraged, the appeal of virtual communication to replace non-urgent visits and ease the workload of medical practitioners is over-powering.
This article will explore the challenges and opportunities telehealth software presents in our collective fight against a rampaging global pandemic—highlighting how custom digital product solutions can accommodate remote care pathways for patients.
DEFINITION
What is telehealth?
A portmanteau of the words telecommunication and healthcare, telehealth is a term that refers to any use of virtual communications infrastructure in various medical practices. Such technology ranges from a bespoke online healthcare consultation portal to an internal software system that manages ancillary services, such as medical training, logistics, patient records, and payment processes.
Often, telehealth and telemedicine are used interchangeably, but the terms differ in scope and definition. Telehealth is a broad term encompassing various technology-assisted services for clinical and non-clinical work conducted remotely. In contrast, telemedicine explicitly denotes implementing off-site technology to deliver direct patient care, from diagnosis and consultation to treatment and monitoring. Telemedicine is part of telehealth, but not all telehealth applications are telemedicine.
Understanding this distinction is crucial for healthcare providers in determining the future parameters of their custom healthcare software. Given the complexity of digital health services, knowing what you need early on would reduce development costs and time-to-market, as the focus should be on designing and integrating features that genuinely address your business concerns.
FEATURES
Key features of telehealth solutions
Custom virtual care software is typically composed of web and mobile applications that deliver functions for patients and providers.
Here are some of the most important features of custom telehealth solutions:
- EHR/EMR: Electronic health/medical or digital health records allow patients and providers to view and access medical data securely.
- Appointment management tools: Everything from patient registration through billing is automated for patients and providers.
- E-prescription: Both patients and physicians benefit from a centralized, digitized (paperless) system to issue and handle e-prescriptions.
- Community health service guide: Provide your patients with a digital roadmap of your services so it’s easier for them to direct their care.
- Video/audio/text-based care management: Video, audio, and text-based messaging services form the basis of virtual care.
- Geolocation: Geolocation services help physicians confirm a patient’s physical location.
Telehealth services in times of Covid-19
Sprung out of necessity, the uptake of telehealth is a direct response to the Covid-19 lockdown.
Experts underscore three main areas that have propelled this industry demand:
- Positive public response to a contactless commercial telehealth service.
- Steady influx of providers and practitioners with an established telehealth infrastructure.
- A regulatory framework promulgating telehealth adoption through coverage waivers, approvals of new services, and parity reimbursement.
The use of telehealth rose by 38%, both periodic and outpatient visits, compared to the pre-pandemic baseline — with variations of 13 to 17% across specialties, according to the global management consultancy McKinsey & Company.
Apart from the lower risk of exposure to COVID-19, the consumers’ growing preference for telehealth also comes from the demand for streamlined medical services. In 2020, nearly eight out of ten consumers disclosed their interest in going digital for healthcare assistance—a significant jump from only 11% in the year prior.
Interestingly, primary care physicians stand to benefit the most from virtual care options, with 97% of them moving their medical operations digitally in 2020 compared to frontline medical operatives at only 57%.
BENEFITS
The manifold advantages of telehealth apps
The benefits a telehealth app provides are manifold and far-reaching, not just in clinical processes but also in administrative and managerial functions.
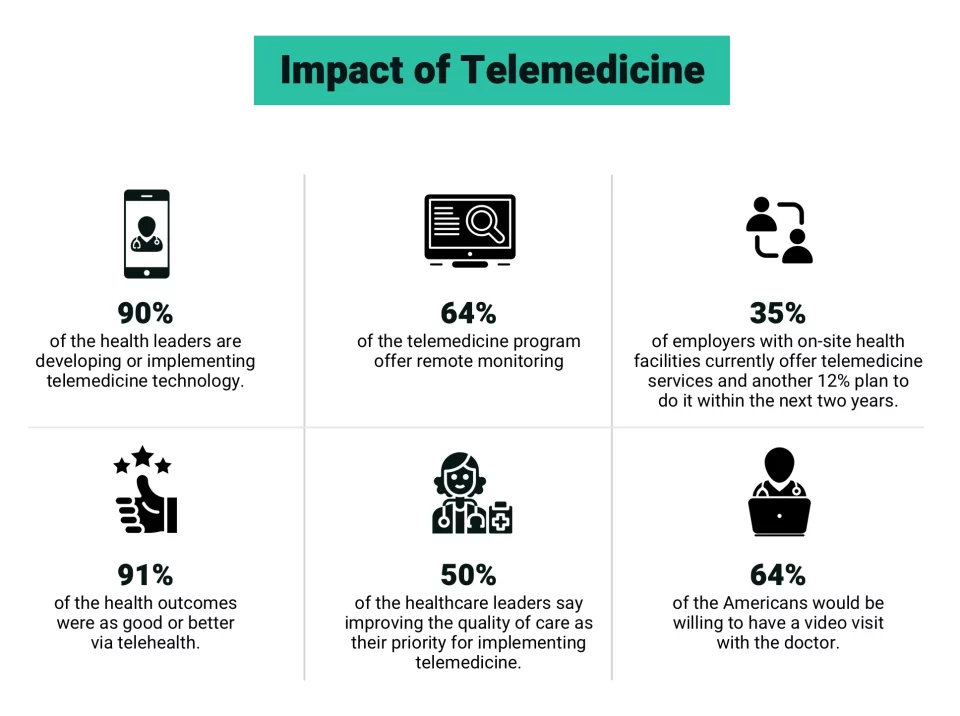
Technology is enabling healthcare transformation
Here are a few reasons why investments in telehealth software are worth considering:
- More receptive to digital transformation – Telehealth is part of a larger blueprint that envisions digitalization as the future of healthcare. By embracing this technological shift early on, healthcare organizations would better adapt to the increasingly complex challenges in medical care and the coming waves of other digital disruptors, such as AI-powered wearables and IoT-enabled medical equipment. With robust digital capabilities, medical providers can gain a competitive edge in new clinical research and advancement areas.
- Better patient engagement and health awareness – Equipped with built-in assistive tools like high-quality video conferencing platforms and accessible personal medical information, health apps encourage patients to be more involved with their health and give them the liberty to choose their physicians from a group of specialists. This user-focused customizability, in turn, leads to better patient engagement and health awareness.
- Enhanced outpatient care – As the demand for affordable and hassle-free outpatient care has grown exponentially in the past few years, healthcare providers turn to medical apps to facilitate medical access to patients in the comfort of their homes whenever convenient. This ambulatory care option benefits those with mobility restrictions due to chronic conditions, those requiring limited yet in-demand specialized care, and those living in rural areas sans proper medical facilities.
- More streamlined healthcare services – Most telehealth apps possess a high degree of automation and system integration to accelerate clinical workflow. By assigning various administrative tasks to preprogrammed software commands and integrated modules, like retrieving medical records from an external database to display on the user’s interface, practitioners can concentrate on faster patient diagnosis and treatment delivery.
- Lower operational costs – Owing to the minimum operational logistics required, proprietary health apps enable healthcare organizations to offer quality care at a fraction of the costs of on-site medical services.
CHALLENGES
Key development areas in custom telehealth
Telehealth is among the fastest-growing areas in medical technology, with many specialties looking to venture into digital alternatives. Despite the myriad opportunities, custom mobile telehealth software still comes with its development challenges. Being cognizant of these potential drawbacks would enable healthcare organizations to build a more resilient application with well-suited features to their target demographics. These challenges are as follows:
Security protocols
Personal health information is the backbone of virtual care. Keeping the integrity of this data against cyber threats requires custom telehealth solutions to secure their access points with several technical safeguards. In certain jurisdictions, adherence to existing privacy laws, such as GDPR and HIPAA, is mandatory, further underscoring the importance of airtight security protocols.
In most instances, the standard password system isn’t sufficient to keep suspicious activities at bay. Most telehealth apps must now be equipped with multi-factor authentications to see the concurrent use of a password and a code from an authorized device. Software developers can also design a solution that accommodates biometric authorizations readily available in most smart devices, such as fingerprints and facial recognition.
System integration
Software programs that host multiple functionalities cannot function alone. System integration is sometimes necessary to keep the programs running smoothly, and that often goes beyond integrating access to an external EHR database.
For instance, mobile pharmacy apps must be calibrated with online banking APIs and other digital payment services to process payments and orders. For ease of access, these programs can be linked to social media and email APIs, which allow first-time users to access services instantly without creating a new account.
Accessibility
Telehealth software can maximize its demographic outreach by accommodating diverse platforms however, compatibility with multitudes of operating systems can also be costly, so always design your telehealth software for platforms your target audience would most likely use.
With so many aspects to consider, customizing your telehealth might seem daunting but with expert help, it is quite feasible.
CONCLUSION
Telehealth is here to stay
It’s abundantly clear that both patient consumers and their healthcare providers love the convenience of virtual care visits.
Telehealth usage is continuing to skyrocket. While the pandemic created the perfect conditions for many consumers to try telehealth services, these solutions will continue to be a regular part of everyday life in the post-pandemic world.
Organizations that harness the true potential of telehealth will be best positioned to lead the market in the coming years. So,keep agile competitors from getting the better of you;embrace virtual care, the future of person-centered medical services.






